Students
- Colin Lin
- Jeep Narongthanarath
- Haruka Tomoeda
Professor
- Yusuke OBUCHI
Course Assistants
- Toshikatsu KIUCHI
- So SUGITA
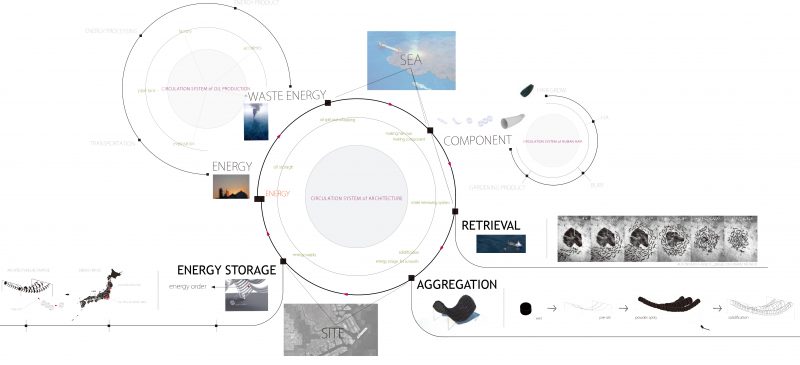
Human hair is collected and it is woven into a fabric-like material. These hair components are then used to retrieve oil from oil spills in the ocean. Following retrieval, soft rubber tubes form a geometry around the oil-soaked hair. The resulting architecture thus stores the energy of the oil and also makes a public space.
髪の毛が収集され、生地のような素材に織り込まれています。毛髪のコンポーネントは、海洋における油流出から油を回収するために使用されます。回収された後、油を吸収した髪の周りに柔らかいゴム製の管でジオメトリを形成します。結果、作成されるアーキテクチャはこうして油のエネルギーを格納し、パブリック スペースになります。
Hair is collected as a key material. It is under-utilized, has highly absorbent properties, and exhibits potential as a phase-changing material. The oil from oil spills is hazardous and is detrimental to both the local and global environment. It is damaging to wildlife, plants, and oceans. It also indicates economic loss. It affects water supplies in communities.
髪がキー マテリアルとして収集されます。髪は活用されていない資源です。高い吸収性があり、相変化材料として使用できる可能性を有しています。オイルスピルからの油は危険で、ローカルとグローバル両方の環境に有害です。野生動物、植物や海に有害のみならず経済的損失を示します。また、コミュニティの水供給に影響します。
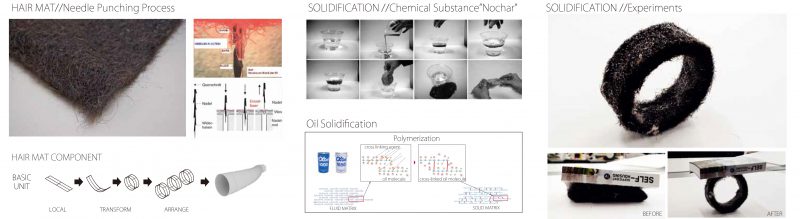
Hair is collected (from donations) and is then punched into a fabric-like material and used to create hair booms. It is covered in a solidifying agent such that when it absorbs oil in the intended application, it hardens after a period of approximately two weeks. The hardened components can then be stored and shaped. In this way, oil can be safely stored and the hair finds a new application.
寄付から収集された毛は、生地のような素材に圧縮され、髪ブーム(浮き)を作成するために使用します。さらに、特殊な凝固剤で覆われており、目的としていた油を吸収して約 2 週間経った後に固まります。硬化した部品は、保存および形成することができます。したがって、油を安全に保存することができる髪の毛は、新しい利用法を得ることができました。
The hardened hair/oil components are covered in a soft rubber and are formed into catenary arches. These function as public gathering spaces.
硬化した髪・石油コンポーネントは柔らかいゴムで覆われ、カテナリー・アーチを形成しています。これらは公共のスペースとして機能します。
The catenary arch structures act as energy storage facilities. In times of emergency, the structure can be disassembled for use as fuel and the oil soaked booms can be shipped to locations in need of energy. Additionally, the scheme would have the benefit of cleaning up the environment in the local area. More land in the area could be public use, facilitated by the addition of new community gathering spaces.
カテナリー・アーチの構造体は、エネルギーを温存する設備として機能します。緊急事態時、構造を分解することでエネルギーを必要としている場所に燃料として使用するために石油を吸収したブームを出荷することができます。さらに、この一連の流れは、周辺環境のクリーンアップの利点があります。より多くの場が地域の公共の場として使用でき、新しいコミュニティが集まるスペースの増加が見込まれます。

Students • Olesia Biloborodko • Trudy Ko • Deli Zhao Professor • Yusuke OBUCHI Course Assistants • Toshikatsu KIUCHI • So SUGITA
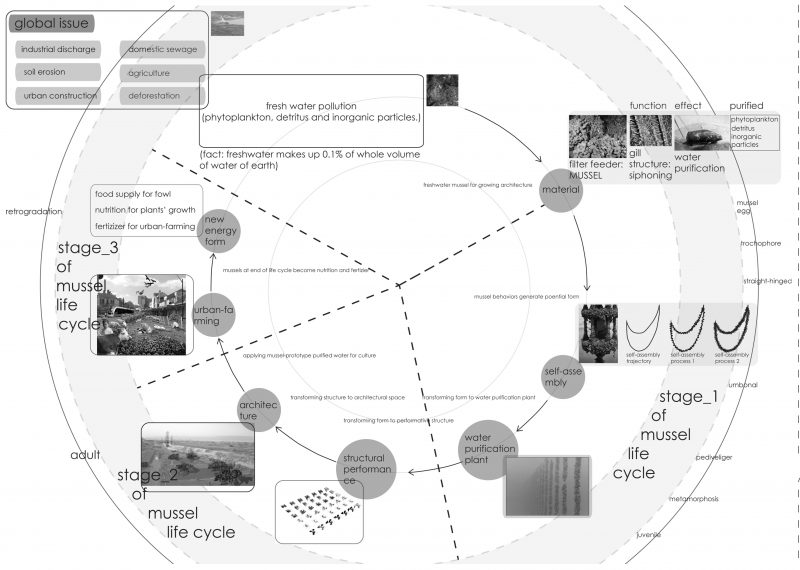
Mussels are used to produce architecture. There are three phases to the architecture. Phase 1 is the mussel growing phase, during which water is purified. Phase 2 is the mussel solidifying phase, where the mussels become a structural system and their architectural characters can be shaped. Phase 3 is the mussel decomposition phase, where energy is produced.
ムール貝を建築的に使用しています。この建築には、 3 つのフェーズがあります。フェーズ 1 は、ムール貝の成長段階で水が浄化されます。フェーズ 2 は、ムール貝の硬化段階による構造システムの形成と建築的要素が形作られる段階です。フェーズ 3 は、ムール貝が分解しエネルギーを生成するものです。
Mussels are shallow water organisms that live at a maximum depth of 10 meters. They are most abundant at or near low tide level, where their food supplies are most concentrated. One mussel can clean four liters of water per hour. In aggregate, there is potential for mussels to address issues such as industrial discharge, soil erosion, and domestic sewage. Polluted fresh water, which makes up just 0.1% of earth’s water could be cleansed with mussels. A waste water purification plant can clean 80,000 liters of water per day, the equivalent to 1000 mussels.
ムール貝。最大10 メートルの深さに生息する浅海生物。食糧が最も豊富な干潮もしくはそれ以下の深さで集中して生息している。1つムール貝で4リットルの水を1時間で浄化できます。ムール貝の群集体は、産業廃棄物、土壌浸食、生活排水などの問題を解決する可能性があります。地球上の水の0.1%を占めている汚染された淡水は、ムール貝で浄化することが可能です。従来の浄水場は、1日80,000リットルの水を浄化でき、ムール貝1000匹に相当します。
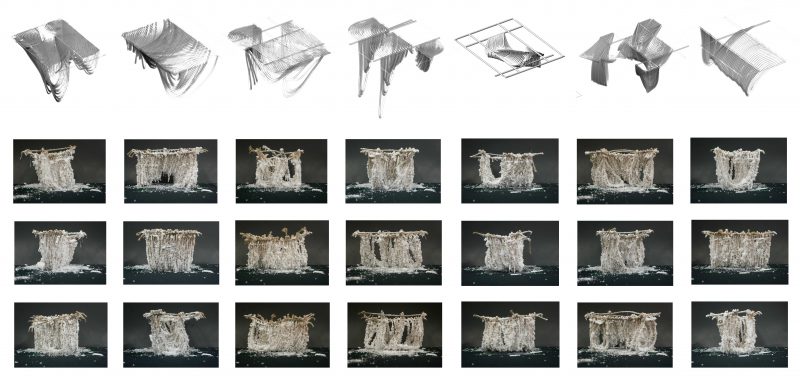
Mussels must be gathered together on a series of ropes to form catenary curves. The mussels self-assemble on lines and harden in place, during which phase the water is purified. Through this process, the mussel element (in aggregate) gains the ability to act as an architecture.
ムール貝を縄に収集することでカテナリー曲線の構造を形成する必要があります。ムール貝は一列に自己形成し、その場で硬化するうちに水を精製する段階に入ります。このプロセスで群集したムール貝の要素は、建築として機能する能力を得ます。
Once hardened into the catenary curve position underwater, the mussel lines gain the ability to perform as architecture. What was once a water purification system becomes a canopy structure. The catenary curves are removed from the water and are turned upside down to produce a canopy structure. In this phase of the project life cycle, the mussels’ primary function is to fulfill a role as architecture.
一度カテナリー曲線に固まったムール貝のラインは、建築的要素として機能できる可能性を得ます。かつて水浄化のためだったシステムは日陰/キャノピー構造になります。水中でカテナリー曲線に固定された硬化後のムール貝は、水揚げされた後に逆さまにすることでキャノピー構造になります。本プロジェクトのライフ・サイクルで、この段階でのムール貝の主な役割は、建築として機能することです。
In the third and final stage of the project life cycle, where the mussels decompose, the material becomes a resource for farming and agriculture by acting as a nutrition source. It is food supply for birds and fertilizer for farms. The project thus provides fresh water, a community gathering space, and a food/fertilization resource at different stages of the project life cycle.
このプロジェクトのライフ・サイクルの3番目で最後の段階でムール貝は分解し、肥料や栄養源として農作物と農業のリソースとして使用できます。鳥のための食糧、植物のための栄養分、農場の肥料などとして利用できます。したがって、このプロジェクトは、ライフ・サイクルの各段階を通して新鮮な水、食料や肥料のリソース、コミュニティの集会スペースなど提供できます。


Students
- Akinori Hamada
- Taichi Kuma
- Shuhei Tanaka
Professor
- Yusuke OBUCHI
Course Assistants
- Toshikatsu KIUCHI
- So SUGITA
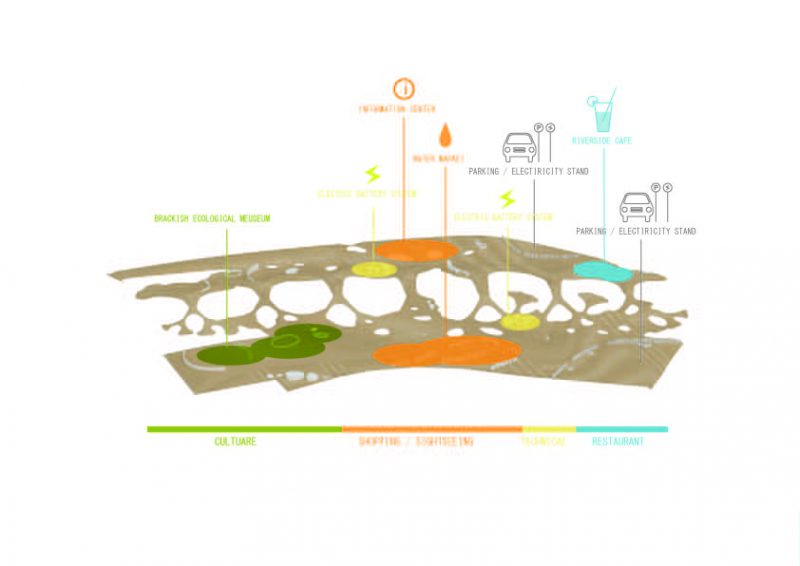
Intro: An electricity plant that generates power through a chemical reaction. Electricity is generated at the point where salt water and factory runoff water meet. The power plant is established as a park and is capable of connecting residential and industrial areas.
イントロ: 化学反応で発電する電力プラント。塩水と工場流出水の合流地点で電気が生成されます。発電所は公園として確立されて、住宅および工業地域と接続することが可能です。
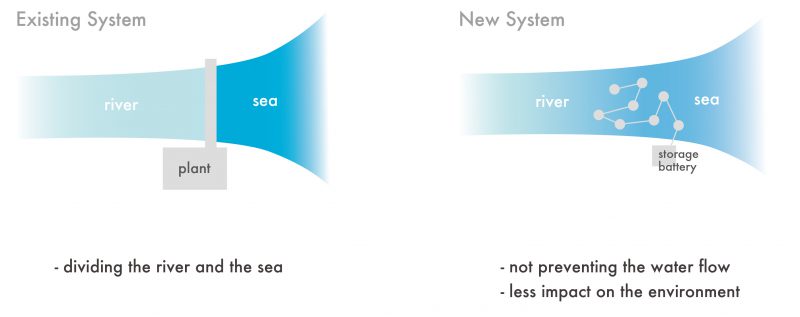
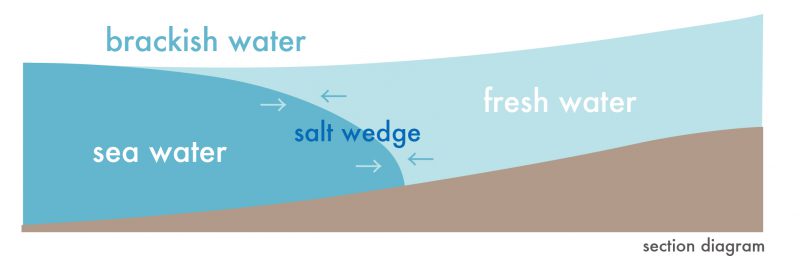
Raw Material: Brackish water at a site where river water and sea water meet. Electricity is produced at this point due to the mixing of salt water and fresh water. Purified water results as a by-product. The existing power plant in the area divides the river and the sea, thus impacting the flow of water and the local environment.
原料:淡水と海水が混ざることで発生する汽水性の水。電気は、この汽水域で淡水と海水の混合で発生します。浄化された水が副産物として精製されます。従前の発電所は川と海を分断してしまうため、汽水を変換・応用することで新しいエネルギー資源となり、従って水の流れおよび周辺環境に良いインパクトを与えます。
Transformed Material: Sea and river water (mixed) pass through a membrane which removes impurities and ions. Purified water is produced through the process.
材質変換:海水や淡水の混合水は、不純物やイオンを除去する膜を通過します。精製水は、このプロセスを経て作られます。
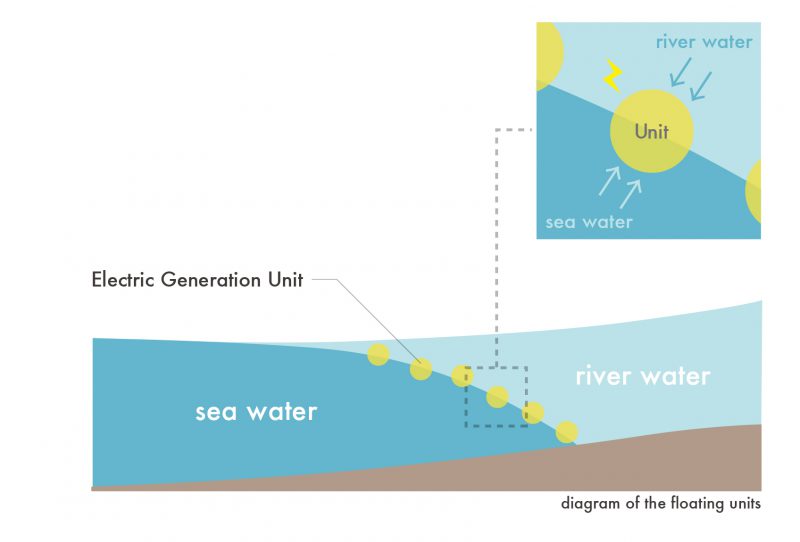
Architectural Prototype: Capsules float on the salty sea water, but beneath the river water. The architecture thus floats on the boundary surface between the two layers. Its level (and thus, the habitable area of the zone) changes with the tides. This creates an adaptive floating bridge which changes position. The membranes required to produce the purified water and the energy are placed inside the floating capsules, which are connected together.
建築的プロトタイプ:カプセルは、海水の上、淡水の下に浮かびます。こ の建築はこうして 2 つの層の境界面に浮かんでいます。カプセルの浮遊深度や居住できるゾーンが潮に応じて変わります。1 日を通して位置が変更する適応型浮体橋が結果としてできます。精製水とエネルギーを生成するために必要な膜は、浮動カプセルに内蔵され、全カプセルは接続されている。
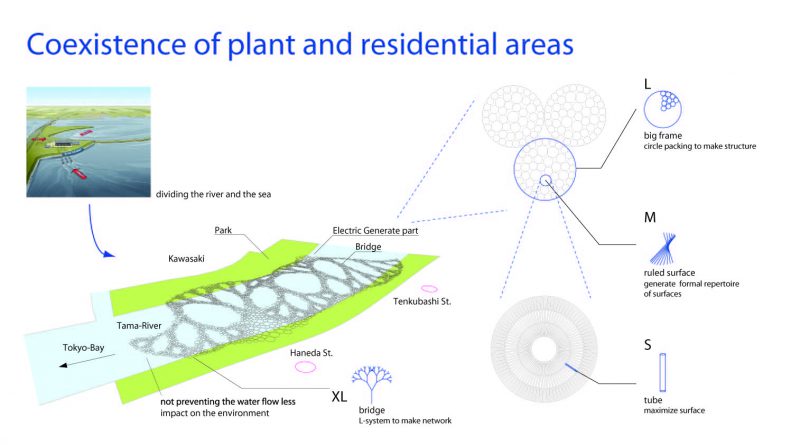
Urban Prototype: The power plant generates energy, provides purified water, and creates an adaptive bridge space. It can connect residential and industrial areas and provide a community center around which shopping and educational facilities can be situated. Because of the shifting tide levels, the area can provide an interesting user experience. It can boost the local economy with shopping and sightseeing, in addition to generating power.
都市的プロトタイプ:この発電所は、エネルギーを生成し、精製水を提供し、適応型浮体橋の空間を作成します。それを周辺の住宅や工業地域に接続することで、ショッピング、教育や利便性の高いプログラムに囲まれたコミュニティ センターができます。潮の満ち干きで変化する高低差によって、興味深いユーザー エクスペリエンスを提供できます。それは、発電に加え、ショッピングと観光といった地域経済を高める要素に寄与できます。


Lecture: Geometry Topology Materiality; the structural parameters in a collaborative design approach Speaker: Klaas de Rycke, Structural Engineering, BOLLINGER + GROHMAN May 7, 2012 13:00-14:30




